We are at the beginning of a new chapter of the internet age. A new platform that «will be even more immersive; an internet in which the user is part of the experience and does not just watch it». These words by Facebook number one Mark Zuckerberg, spoken at the now famous Connect conference in October 2021, were enough to consecrate the metaverse as the “next big thing” in the digital world, attributing himself the role of pioneer by launching Horizon Worlds, a virtual space that can be accessed with your Facebook account and wearing Oculus viewers (a company acquired by Facebook itself, now Meta, already in 2014).
Talking about the metaverse today, Wired argues, is a bit like talking about the internet in the 1970s. This experience is made possible by a mix of devices and infrastructures: augmented reality (AR, i.e. the one that enriches the real world with virtual elements), virtual reality (VR, i.e. the entirely digital one, visible through the so-called “goggles”), connection superfast 5G, blockchain…
However, it doesn’t end with any of them.
Source- data Bridge Market Research
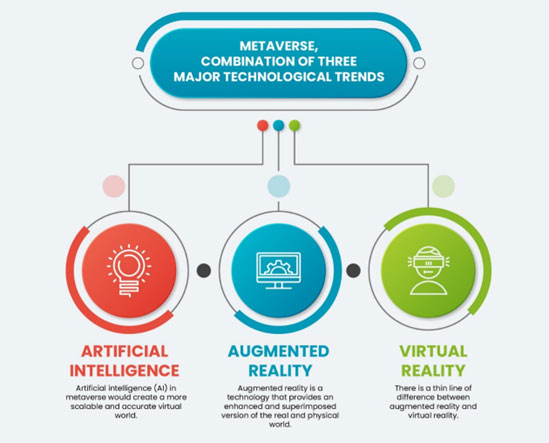
Figure 1: what’s the metaverse?
By metaverse we mean an interconnected digital experience that integrates and works with the real world and that does not use a specific type of technology, but exploits different ones, for a completely immersive experience.
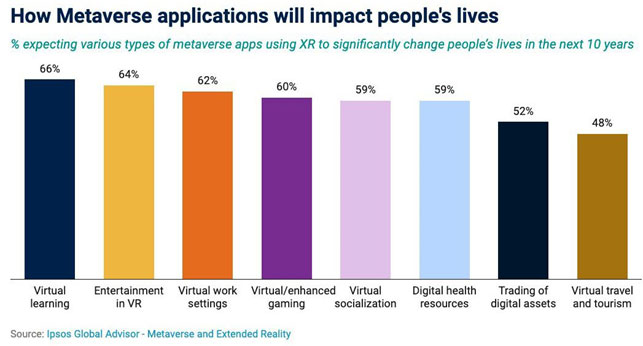
The Metaverse is the next evolution of the Internet:
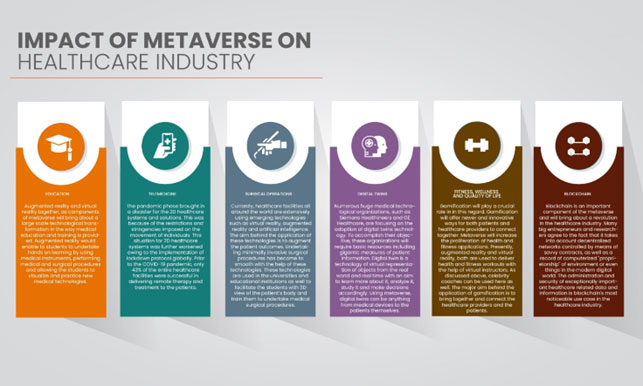
This development, which until now has been limited to science fiction and video games, will change every sector, including the smallest aspects of everyday life: from work to healthcare, from education to personal relationships.
The metaverse will increasingly enable work on personalized and precision medicine that gives people the opportunity to create a personalized experience to manage their health.
Augmented reality and virtual reality together, as components of the metaverse, could be very useful for training and education by using medical instruments and performing medical and surgical procedures, especially for students. Metaverse could be the future of the telemedicine and opportunity to manage patient at distance and also to improve patient quality of life.
Source: data Bridge Market research
The metaverse in cardiology will be an opportunity to better study the heart, the digital gives the possibility of having the possibility of visualizing the cardiac structure from every angle, from every direction, from every position, you can even enter the heart organ, if you have to correct a heart sometimes very small the possibility of enlarging it allows you to look better where to go.
The metaverse is certainly virtual but the impact is real.

e-Health (electronic health) refers to the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) to promote organizational change and facilitate new healthcare skills.
In the last few years, several telemedicine services using ICT have been launched and the updating of related regulations has started, also for the increase in demand for services, their complexity and the need to offer adequate care to the patient.[1]
One of the main objectives of digital healthcare is to make it more usable and fairer on the national territory, simplifying care pathways.
In Italy, according to the mapping of telemedicine experiences on the national territory drawn up in 2018, telemonitoring and teleassistance represent 26% of telemedicine services; 43% of them concern the specialist cardiological field and in 45% of cases involve patients with chronic pathologies.
Support systems for therapy with the use of technology help adherence to therapy and also strengthen the doctor-patient dialogue. We live in an era of great changes in medicine: compared to the past, the doctor has access to an immense amount of data on the individual patient. Thanks to the use of wearable devices, we can record and download clinical parameters (heart rate, blood pressure, etc…) and we can learn about daily habits such as physical activity and sleep hours. The use of this data will allow in the future thanks to artificial intelligence to implement new prevention and treatment strategies with an increasingly precise approach to medicine, tailored with sartorial precision on the characteristics of the patient.
Artificial Intelligence in cardiology represents a great opportunity, if further developed in a trustworthy way, to support human intelligence in daily practice. AI could help cardiologists to operate with greater efficacy and efficiency, supporting precision, timeliness, ethics, while meeting all patients’ needs.
AI, however, is not yet so widely disseminated in cardiology and important challenges and obstacles have to be overcome, concerning ethics, conflict of interests, algorithm improvements and transparency, product certification, input processing, cyber security, privacy, and need for collaboration and cooperation of different involved professions, within and between different institutions of heterogeneous complexity.
Nowadays the cardiologist profession is evolving, also acquiring a certain complexity in daily exercise, think of the amount of information and data that the doctor receives thanks to the use of wearable devices that help monitor some clinical parameters such as heart rate and blood pressure to daily habits such as the number of hours you sleep and steps taken each day. There is therefore a constant need to manage immense quantities of data which, combined with the experience of the professional in the field, means having support for medical practice but also training and continuous updating is necessary and fundamental to the profession and is not always possible or available, especially if speaks of highly advanced technologies such as the use of artificial intelligence in cardiology which will really allow the cardiologist to be supported in order to respond to the need for support for daily clinical decisions, through an improvement in diagnostic and prognostic performance increasingly towards the horizon of precision medicine allowing different applications of artificial intelligence in cardiology: from AI models to support risk stratification and clinical decisions, to the application of artificial intelligence to ECG, echocardiography, magnetic resonance in the field of cardiologists co , nuclear cardiology and new future opportunities to be discovered.
[1] E-health, telemedicina e applicazioni in cardiologia: stato dell’arte in Italia ed esperienza dell’U.O.C. di cardiologia dell’Ospedale G.B. Grassi di Roma Pensiero Scientifico Editore -27.05.22 di Fabrizio Ammirati, Manuela Bocchino, Luca Santini, Guglielmo Pastena, Fabio Ferranti, Lazzaro Paraggio, Nicola Danisi.












